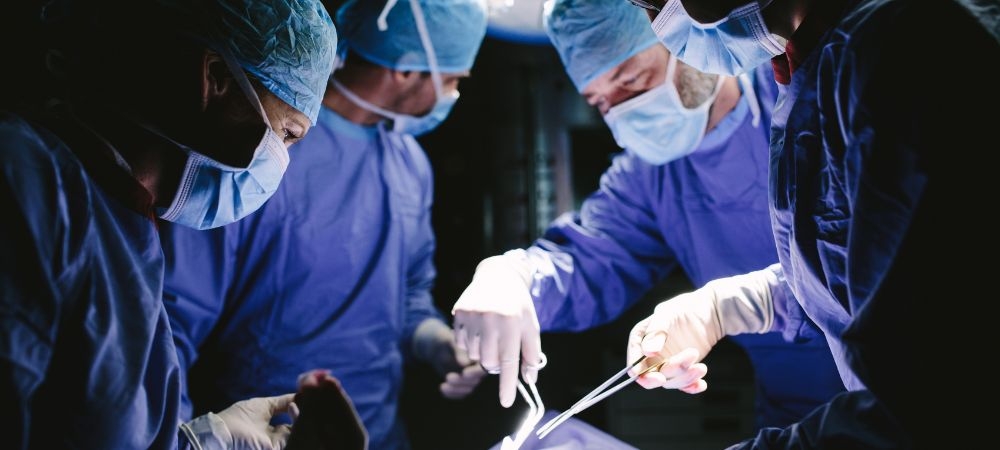

Chronic diseases are long-term health conditions that can significantly impact an individual's daily life and require ongoing management. These conditions are characterized by their gradual onset and persistence, typically lasting three months or longer. Unlike acute illnesses, which appear suddenly and resolve relatively quickly, chronic diseases develop slowly over time and can endure for years, often for a lifetime. Their management often involves continuous medical attention and lifestyle adjustments to mitigate symptoms and prevent complications.
Common examples of chronic diseases include heart disease, diabetes, and chronic respiratory conditions. These illnesses necessitate long-term treatment plans and regular monitoring to manage symptoms effectively. For instance, individuals with heart disease may require consistent medication to control blood pressure and cholesterol levels, alongside lifestyle changes such as dietary modifications and increased physical activity. Similarly, diabetes management often includes routine blood sugar monitoring, a balanced diet, regular exercise, and possibly insulin therapy.
The distinction between chronic and acute conditions lies primarily in their onset, duration, and management approach. Acute conditions, such as infections or injuries, arise abruptly and are generally short-lived, often requiring immediate medical intervention. Once treated, individuals typically recover fully. Diet and nutrition play a significant role in managing chronic diseases. Adopting a balanced and nutrient-rich diet tailored to specific health conditions can help control symptoms and prevent complications. For example, individuals with diabetes should focus on low-glycemic foods that help regulate blood sugar levels, while those with heart disease should emphasize a diet low in saturated fats and high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Consulting with a dietitian can provide personalized dietary guidance and support. Facilities offering chronic diseases Utilizing available resources and support networks can enhance navigation efforts. Many organizations and community groups offer resources for individuals with chronic diseases, including educational materials, support groups, and patient advocacy services. Connecting with these resources can provide valuable information, emotional support, and practical assistance in managing the condition.. For example, someone with the flu may experience intense symptoms for a week or two, but once treated, they usually return to their normal health.
In contrast, chronic diseases involve persistent or recurring symptoms that, while they may be less dramatic than those of acute conditions, have a lasting impact on health and quality of life. Managing these diseases usually requires a multidisciplinary approach, integrating lifestyle changes, ongoing medication, and regular health check-ups to monitor and control the condition. The primary focus is on maintaining health, alleviating symptoms, and preventing exacerbations or complications over the long term, which contrasts with the often immediate and transient nature of acute illness treatment.
Among the most prevalent chronic diseases affecting adults today are cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, chronic respiratory diseases, and certain types of cancer. These conditions pose significant public health challenges due to their widespread occurrence and potential to lead to severe complications and diminished quality of life.
Cardiovascular diseases, including heart disease and stroke, rank among the leading causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Risk factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, and obesity contribute to these conditions. Effective management involves lifestyle changes like adopting a heart-healthy diet, regular physical activity, and adherence to prescribed medications. Diet and nutrition play a significant role in managing chronic diseases. Adopting a balanced and nutrient-rich diet tailored to specific health conditions can help control symptoms and prevent complications. For example, individuals with diabetes should focus on low-glycemic foods that help regulate blood sugar levels, while those with heart disease should emphasize a diet low in saturated fats and high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Consulting with a dietitian can provide personalized dietary guidance and support. Facilities offering chronic diseases Utilizing available resources and support networks can enhance navigation efforts. Many organizations and community groups offer resources for individuals with chronic diseases, including educational materials, support groups, and patient advocacy services. Connecting with these resources can provide valuable information, emotional support, and practical assistance in managing the condition.. In some cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to address severe complications such as blockages in the arteries.
Definition: Chronic diseases are long-lasting conditions that typically last three months or more and require ongoing management.
Onset and Duration: Unlike acute conditions, chronic diseases develop gradually and can persist for years or a lifetime.
Impact on Daily Life: These diseases often necessitate continuous medical attention and lifestyle adjustments, significantly altering daily functioning.
Common Examples: Common chronic diseases include heart disease, diabetes, chronic respiratory conditions, and certain types of cancer.
Management Approach: Managing chronic diseases usually requires a multidisciplinary approach involving lifestyle changes, medication, and regular check-ups.
Physical Symptoms: Chronic diseases can lead to persistent symptoms like pain, fatigue, and physical impairments that affect daily activities.
Emotional Challenges: Living with a chronic disease can lead to increased stress, anxiety, and depression, impacting mental health and self-esteem.
Lifestyle Modifications: Individuals often need to adhere to treatment plans, make dietary changes, and incorporate regular exercise into their routines.
Healthcare Navigation: Understanding the healthcare system is crucial for effective management, involving education about one’s condition and treatment options.
Primary Care Relationship: Establishing a strong relationship with a primary care provider is essential for coordinated and comprehensive care.
Health Record Organization: Keeping organized records of medical history, medications, and treatments is vital for continuity of care.
Appointment Management: Proactively scheduling and managing appointments with healthcare providers is critical for timely care.
Insurance Understanding: Familiarity with health insurance coverage is necessary to make informed decisions about care and manage costs.
Self-Advocacy: Advocating for oneself during medical appointments helps ensure that needs and concerns are addressed.
Support Networks: Utilizing support groups and resources can provide emotional support and practical advice for managing chronic conditions.
Role of Nutrition: A balanced diet tailored to specific health needs can significantly impact the management of chronic diseases.
Mindfulness Practices: Techniques like meditation and yoga can help manage stress and improve emotional well-being.
Physical Activity: Regular exercise tailored to individual abilities can enhance overall health and help manage symptoms.
Preventive Care Importance: Regular screenings and check-ups can help detect complications early, allowing for timely interventions.
Meaningful Engagement: Pursuing hobbies and community activities fosters a sense of purpose and enhances quality of life for individuals with chronic diseases.
Diabetes is another significant chronic condition characterized by elevated blood glucose levels resulting from insufficient insulin production or insulin resistance. The most common form, Type 2 diabetes, is often associated with obesity, sedentary lifestyles, and genetic predisposition. Effective management includes regular blood sugar monitoring, a balanced diet rich in whole foods, regular physical activity, and adherence to medications to control glucose levels. Facilities offering chronic diseases . Poorly managed diabetes can lead to severe complications, including cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, and neuropathy.
Chronic respiratory diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma can severely affect lung function and overall respiratory health. COPD is typically caused by long-term exposure to harmful substances like tobacco smoke, while asthma may be triggered by allergens and environmental factors. Management strategies focus on controlling symptoms, minimizing exposure to known triggers, and utilizing medications such as bronchodilators and corticosteroids to maintain open airways.
Certain cancers, including breast, prostate, and colorectal cancer, exhibit chronic characteristics as well. While treatment approaches have advanced significantly, many cancer patients require ongoing monitoring and management due to the risk of recurrence or metastasis. Treatment modalities may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapies tailored to the specific cancer type and stage.

Effectively managing these chronic diseases necessitates comprehensive strategies that encompass preventive measures, early detection, and continuous care. Lifestyle factors play a critical role in the development and management of these conditions, influencing health outcomes through behaviors that can either protect against or increase the risk of chronic diseases. Key lifestyle factors include diet, physical activity, smoking, and alcohol consumption. Healthy eating, regular exercise, avoiding tobacco, and moderating alcohol intake can significantly reduce the risk of developing chronic conditions and enhance overall well-being. Understanding and addressing these lifestyle factors is essential for both prevention and effective management of chronic diseases, emphasizing the importance of a proactive approach to health.
In addition to lifestyle factors, psychological and social determinants also play a crucial role in the development and management of chronic diseases. Mental health conditions, stress, and socioeconomic status can influence an individual's ability to maintain healthy behaviors, adhere to treatment plans, and access necessary healthcare resources. For instance, those experiencing chronic stress may be more likely to engage in unhealthy coping mechanisms, such as overeating or smoking, which can exacerbate chronic conditions.
Social support networks, including family, friends, and community resources, significantly impact an individual's ability to manage chronic diseases effectively. Support from loved ones can encourage adherence to treatment plans, promote healthier lifestyle choices, and provide emotional reassurance during difficult times. Community resources, such as support groups or wellness programs, can also offer valuable education and motivation for individuals navigating their health challenges.
Chronic kidney disease may initially show subtle signs like changes in urination patterns, such as increased frequency or foamy urine. Other early symptoms can include swelling in the hands or feet, unexplained fatigue, and difficulty concentrating. As kidney function declines, individuals might experience persistent nausea, poor appetite, and changes in skin color. Early detection through routine kidney function tests can be crucial in managing the disease effectively. Facilities offering chronic diseases Navigating the healthcare system effectively can be challenging for individuals with chronic diseases, but several strategies can help manage the process and ensure they receive appropriate care. Understanding the system, actively participating in one's own care, and leveraging available resources are key components of effective navigation..Education and awareness are essential components of managing chronic diseases. Empowering patients with knowledge about their conditions enables them to make informed decisions regarding their health. Educational initiatives can include information on the nature of their illness, potential complications, management strategies, and the importance of regular medical follow-ups. This empowerment fosters a sense of control and encourages proactive participation in one's own health management.
Moreover, advancements in technology have transformed the way chronic diseases are monitored and managed. Wearable devices and mobile health applications allow individuals to track vital signs, monitor symptoms, and receive reminders for medication and appointments. Being proactive in managing appointments and referrals is critical. Individuals should schedule regular check-ups with their primary care provider and any necessary specialist appointments. It is important to follow up on referrals, test results, and treatment recommendations promptly. Keeping a calendar or planner to track appointments, deadlines, and follow-ups helps avoid missed appointments and ensures timely care. CureValue Chronic kidney disease may initially show subtle signs like changes in urination patterns, such as increased frequency or foamy urine. Other early symptoms can include swelling in the hands or feet, unexplained fatigue, and difficulty concentrating. As kidney function declines, individuals might experience persistent nausea, poor appetite, and changes in skin color. Early detection through routine kidney function tests can be crucial in managing the disease effectively.. Telemedicine has also expanded access to healthcare, enabling patients to consult with healthcare professionals from the comfort of their homes, which is particularly beneficial for those with mobility issues or those living in remote areas.
Preventive measures are vital in reducing the incidence of chronic diseases. Public health initiatives aimed at promoting healthy behaviors-such as smoking cessation programs, physical activity campaigns, and nutritional education-are essential to curb the rising rates of these conditions. Regular screenings and early detection efforts can help identify chronic diseases in their early stages, allowing for timely intervention and better outcomes.
The economic impact of chronic diseases cannot be overlooked. These conditions often lead to increased healthcare costs due to frequent medical visits, hospitalizations, and the need for long-term care. Additionally, chronic diseases can affect productivity, leading to absenteeism or reduced work capacity, which can further strain individuals and families financially. Thus, addressing chronic diseases effectively not only improves individual health outcomes but also alleviates broader economic burdens on healthcare systems and society.
In conclusion, chronic diseases represent a significant and growing challenge to public health. Their complexity demands a multifaceted approach that encompasses medical, psychological, and social strategies. By focusing on prevention, education, and support, individuals can lead healthier lives while managing these conditions effectively. As we continue to learn more about chronic diseases, it becomes increasingly clear that a collaborative approach-one that involves healthcare providers, patients, families, and communities-is essential for promoting long-term health and well-being.
Diet is a fundamental lifestyle factor affecting chronic disease risk. Consuming a diet high in processed foods, saturated fats, sugars, and sodium is associated with an increased risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. Conversely, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help prevent these conditions by providing essential nutrients, antioxidants, and fiber that support overall health and reduce inflammation.
Physical activity is another critical factor in chronic disease prevention. Regular exercise helps maintain a healthy weight, improve cardiovascular health, and regulate blood sugar levels. Sedentary lifestyles, characterized by prolonged periods of inactivity, are linked to a higher risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and some cancers. Engaging in physical activity helps manage weight, strengthens the heart and muscles, and improves overall metabolic function, thereby reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
Smoking is a well-documented risk factor for various chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disease, chronic respiratory conditions, and several types of cancer. Tobacco use contributes to the development of these conditions by causing damage to blood vessels, impairing lung function, and increasing inflammation throughout the body. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce the risk of developing these diseases and improve overall health.
Alcohol consumption also impacts chronic disease risk. Excessive alcohol intake is associated with liver disease, cardiovascular problems, and an increased risk of certain cancers. Moderate alcohol consumption, defined as up to one drink per day for women and up to two drinks per day for men, may have some health benefits, such as reducing the risk of heart disease. However, excessive drinking can lead to serious health issues and should be avoided.
CureValue provides clear and detailed information about costs, procedures, and providers, helping users make informed decisions about their healthcare.
CureValue has 1,046 hospitals and clinics in its network.